0. 목차
* 이 글은 MySQL을 기본으로 예제 및 시나리오를 작성합니다.
목차
1. 낙관적 잠금이란?
1.1 MySQL 엔진 level과 스토리지 엔진 level
- MySQL에서 사용되는 잠금은 크게 스토리지 엔진 레벨과 MySQL 엔진 레벨로 나눠볼 수 있다.
- MySQL 엔진 레벨의 잠금은 모든 스토리지 엔진에 영향을 미치게 되지만 스토리지 엔진 레벨의 잠금은 스토리지 엔진 간 상호 영향을 미치지는 않는다.
- 낙관적 잠금은 InnoDB 스토리지 엔진 잠금의 한 종류이다.
1.2 비관적 잠금과 낙관적 잠금
1.2.1 비관적 잠금
- 현재 트랜잭션에서 변경하고자 하는 레코드에 대해 잠금을 획득하고 변경 작업을 처리하는 방식
- '변경하고자 하는 레코드를 다른 트랜잭션에서도 변경할 수 있다'라는 비관적인 가정을 하기 때문에 먼저 잠금을 획득
- InnoDB는 기본적으로 사용하고 있다.
1.2.2 낙관적 잠금
- 각 트랜잭션이 같은 레코드를 변경할 가능성은 상당히 희박할 것이라고(낙관적으로) 가정한다.
- 우선 변경 작업을 수행하고 마지막에 잠금 충돌이 있었는지 확인해 무제가 있었다면 ROLLBACK 처리한다.
- InnoDB 엔진 자체에서 MVCC를 제공
2. 시나리오

2.1 해당 시나리오의 문제점
- 기본적인 트랜잭션 잠금 level이 REPETABLE READ로 설정이 되어 있다고 해도 LOST UPDATE 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
3. LOCK를 적용하지 않은 낙관적 잠금 예제
- sell과 buy api는 동일한 기능을 함 -> 재고(stock)를 한 개씩 감소
// ProductController.kt
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
class ProductController(
private val service: ProductService
) {
@GetMapping("/test")
fun test(): String {
return "Test"
}
@GetMapping("/buy/{id}")
fun buyProduct(@PathVariable id: Long) {
service.buy(id)
}
@GetMapping("/sell/{id}")
fun sellProduct(@PathVariable id: Long) {
service.sell(id)
}
@GetMapping("/{amount}")
fun addProduct(@PathVariable amount: Int) {
service.add(amount)
}
}// ProductService.kt
@Service
class ProductService(
private val repository: ProductRepository
) {
@Transactional
fun buy(id: Long) {
val product = this.repository.findByIdOrNull(id)
product?.decreaseStock(1)
}
@Transactional
fun sell(id: Long) {
val product = this.repository.findByIdOrNull(id)
product?.decreaseStock(1)
}
@Transactional
fun add(amount: Int) {
repository.save(Product(stock = amount))
}
}// Product.kt
@Entity
class Product(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
val id: Long? = null,
var stock: Int
) {
fun decreaseStock(amount: Int) {
this.stock -= amount
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Product(id=$id, stock=$stock)"
}
}ProductRepository.kt
interface ProductRepository : JpaRepository<Product, Long>
3.1 실행 결과
- 최초 1000개의 재고(stock)가 존재

- 조금 나이스하지 않은 방법이지만 단 sell과 buy를 각각 5번씩 api call을 진행했다.
- 기대했던 결과는 sell 5번 buy 5번을 통해 총 10개의 재고가 없어지길 기대했다.
- 하지만 결과값은 기대했던 결과와는 많이 다른 모습을 보여준다.
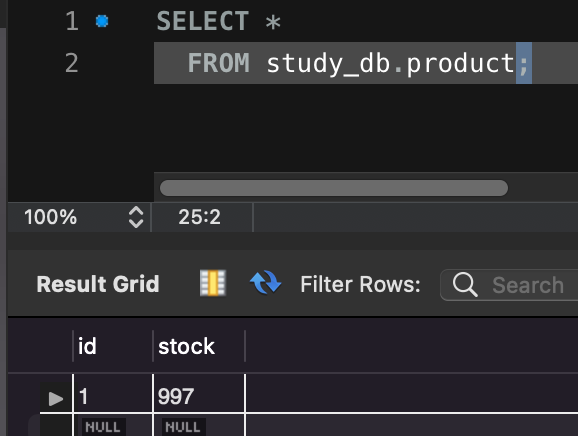
- 이러한 원인은 위에서도 말한 것과 같이 LOST UPDATE 이슈가 발생했기 때문이다.
4 낙관적 LOCK을 사용한 예제
- 위 예제에서 entity 부분에 version annotation을 적용한 field를 추가하고 table에도 version column을 추가하면 된다.
// Product.kt
@Entity
class Product(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
val id: Long? = null,
var stock: Int,
@Version
var version: Int
) {
fun decreaseStock(amount: Int) {
this.stock -= amount
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "Product(id=$id, stock=$stock)"
}
}
- 동일하게 여러 api call을 시도하면 아래와 같이 ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException 이 발생하게 된다.
[Request processing failed; nested exception is org.springframework.orm.ObjectOptimisticLockingFailureException: Batch update returned unexpected row count from update [0]; actual row count: 0; expected: 1; statement executed: update product set stock=?, version=? where id=? and version=?; nested exception is org.hibernate.StaleStateException: Batch update returned unexpected row count from update [0]; actual row count: 0; expected: 1; statement executed: update product set stock=?, version=? where id=? and version=?] with root cause
5. 참고 링크
- https://blog.katastros.com/a?ID=01700-429bf1d9-2dde-4deb-b38b-5df67d568dc5
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=poyjLx-LOEU
- https://m.blog.naver.com/PostView.naver?isHttpsRedirect=true&blogId=parkjy76&logNo=220015135826
- https://dzone.com/articles/what-is-a-lost-update-in-database-systems
- https://vladmihalcea.com/how-does-mvcc-multi-version-concurrency-control-work/
What Is a Lost Update in Database Systems? - DZone Database
dzone.com
How does MVCC (Multi-Version Concurrency Control) work - Vlad Mihalcea
Learn how the MVCC (Multi-Version Concurrency Control) mechanism works using INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE examples from PostgreSQL.
vladmihalcea.com
'IT > 데이터베이스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JPA] failed to lazily initialize a collection (1) | 2022.10.03 |
|---|---|
| [JPA] Null value was assigned to a property exception (0) | 2022.09.18 |
| JPA 공부 - 6 (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| JPA 공부 - 3 (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| JPA 공부 - 5 (0) | 2021.02.07 |



